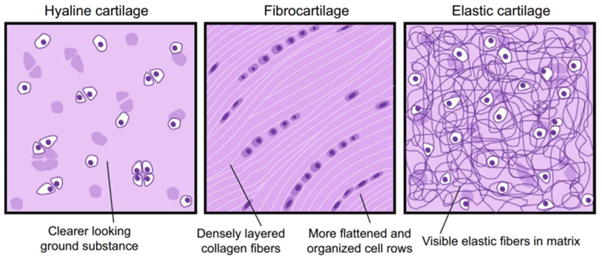
A Photomicrograph Showing The Hyaline Cartilage Fibrous Modern Art Biology Diagrams Cartilage is a strong, flexible connective tissue that protects your joints and bones. It absorbs impacts and reduces friction between bones throughout your body.
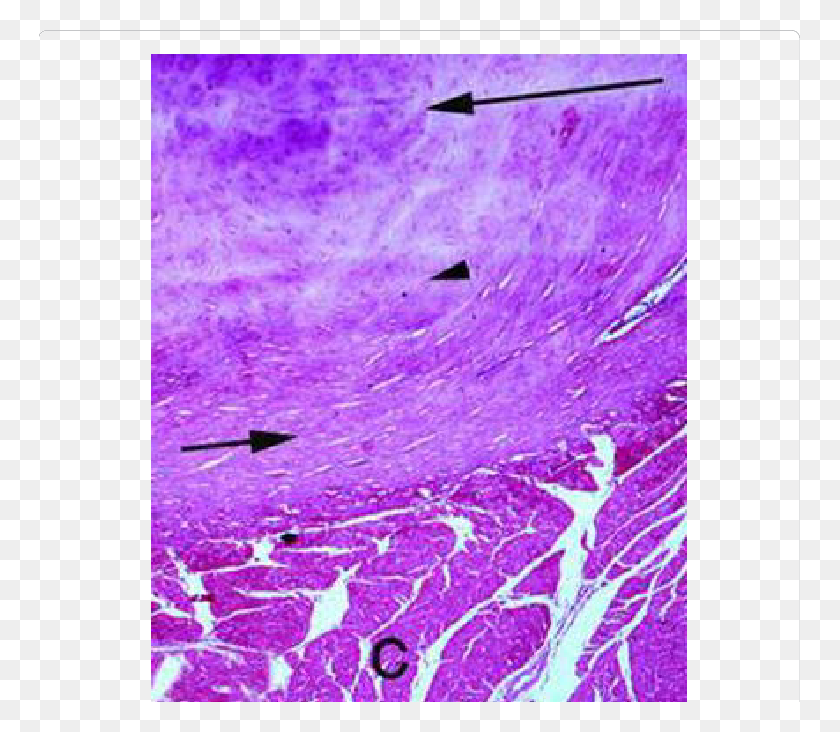
Fibrocartilage is seen in the glenoid labrum, acetabular labrum, menisci, pubic symphysis, etc. Also, in the places where the ligaments and tendons attach to bone. Hyaline Cartilage It is a translucent cartilage that is present on many bone joints. Hyaline cartilage is a firm structure that has collagen. Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue that is stiffer than most other connective tissue types but flexible enough to withstand compressive forces.

Hyaline, Elastic, and Fibro Cartilage Biology Diagrams
Examine this slide of fibrocartilage, noting the distinctive features of fibrocartilage when compared to hyaline and elastic cartilages (see table on previous page 2_2 and the images below). Elastic cartilage resembles hyaline cartilage somewhat in histological appearance with a few subtle differences.
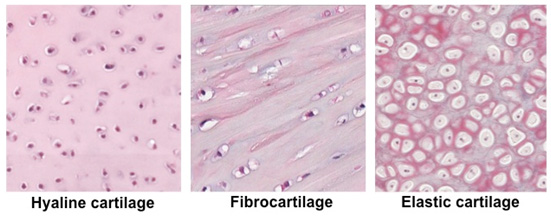
Hyaline cartilage is a type of connective tissue found in areas such as the nose, ears, and trachea of the human body. The word hyaline means "glass-like", and hyaline cartilage is a glossy, greyish-white tissue with a uniform appearance. It is one of the three types of cartilage; the other two types are elastic cartilage and fibrocartilage.

Difference Between Fibrocartilage and Hyaline Cartilage Biology Diagrams
The fibrocartilage provides flexibility, toughness, and elasticity to the structural parts of the body. It contains intermediate characteristics between the dense connective tissue and the hyaline cartilage. The types of cells that occur in the fibrocartilage are fibroblasts, fibrocytes, chondroblasts, and chondrocytes.